反射是怎么影响性能的?
今天来聊聊反射的性能问题。反射具体是怎么影响性能的?
01 反射真的存在性能问题吗?
为了放大问题,找到共性,采用逐渐扩大测试次数、每次测试多次取平均值的方式,针对同一个方法分别就直接调用该方法、反射调用该方法、直接调用该方法对应的实例、反射调用该方法对应的实例分别从 1-1000000,每隔一个数量级测试一次:
测试代码如下:
public class ReflectionPerformanceActivity extends Activity{
private TextView mExecuteResultTxtView = null;
private EditText mExecuteCountEditTxt = null;
private Executor mPerformanceExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
private static final int AVERAGE_COUNT = 10;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_reflection_performance_layout);
mExecuteResultTxtView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.executeResultTxtId);
mExecuteCountEditTxt = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.executeCountEditTxtId);
}
public void onClick(View v){
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.executeBtnId:{
execute();
}
break;
default:{
}
break;
}
}
private void execute(){
mExecuteResultTxtView.setText("");
mPerformanceExecutor.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
long costTime = 0;
int executeCount = Integer.parseInt(mExecuteCountEditTxt.getText().toString());
long reflectMethodCostTime=0,normalMethodCostTime=0,reflectFieldCostTime=0,normalFieldCostTime=0;
updateResultTextView(executeCount + "毫秒耗时情况测试");
for(int index = 0; index < AVERAGE_COUNT; index++){
updateResultTextView("第 " + (index+1) + " 次");
costTime = getNormalCallCostTime(executeCount);
reflectMethodCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行直接调用方法耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getReflectCallMethodCostTime(executeCount);
normalMethodCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用方法耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getNormalFieldCostTime(executeCount);
reflectFieldCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行普通调用实例耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
costTime = getReflectCallFieldCostTime(executeCount);
normalFieldCostTime += costTime;
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用实例耗时:" + costTime + " 毫秒");
}
updateResultTextView("执行直接调用方法平均耗时:" + reflectMethodCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用方法平均耗时:" + normalMethodCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行普通调用实例平均耗时:" + reflectFieldCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
updateResultTextView("执行反射调用实例平均耗时:" + normalFieldCostTime/AVERAGE_COUNT + " 毫秒");
}
});
}
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
try{
Method setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
setmLanguageMethod.setAccessible(true);
setmLanguageMethod.invoke(programMonkey, "Java");
}catch(IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(InvocationTargetException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
try{
Field ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
ageField.set(programMonkey, "Java");
}catch(NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getNormalCallCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
programMonkey.setmLanguage("Java");
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getNormalFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
programMonkey.mLanguage = "Java";
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private void updateResultTextView(final String content){
ReflectionPerformanceActivity.this.runOnUiThread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
mExecuteResultTxtView.append(content);
mExecuteResultTxtView.append("\n");
}
});
}
}
测试结果如下:
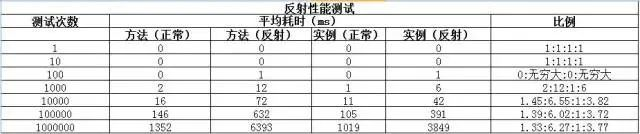
测试结论:
反射的确会导致性能问题。反射导致的性能问题是否严重跟使用的次数有关系,如果控制在100次以内,基本上没什么差别,如果调用次数超过了100次,性能差异会很明显。
四种访问方式,直接访问实例的方式效率最高;其次是直接调用方法的方式,耗时约为直接调用实例的 1.4 倍;接着是通过反射访问实例的方式,耗时约为直接访问实例的 3.75 倍;最慢的是通过反射访问方法的方式,耗时约为直接访问实例的 6.2 倍。
02 反射到底慢在哪?
跟踪源码可以发现,四个方法中都存在实例化ProgramMonkey的代码,所以可以排除是这句话导致的不同调用方式产生的性能差异;通过反射调用方法中调用了setAccessible方法,但该方法纯粹只是设置属性值,不会产生明显的性能差异;所以最有可能产生性能差异的只有getMethod和getDeclaredField、invoke和set方法了,下面分别就这两组方法进行测试,找到具体慢在哪?
首先测试invoke和set方法,修改getReflectCallMethodCostTime和getReflectCallFieldCostTime方法的代码如下:
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
Method setmLanguageMethod = null;
try {
setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
setmLanguageMethod.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int index = 0; index < count; index++) {
try {
setmLanguageMethod.invoke(programMonkey, "Java");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
Field ageField = null;
try {
ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int index = 0; index < count; index++) {
try {
ageField.set(programMonkey, "Java");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
}
沿用上面的测试方法,测试结果如下:
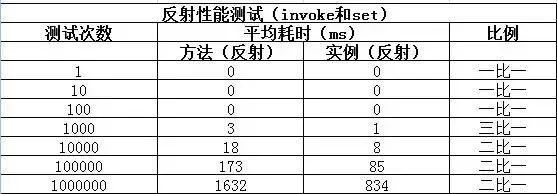
修改getReflectCallMethodCostTime和getReflectCallFieldCostTime方法的代码如下,对getMethod和getDeclaredField进行测试:
private long getReflectCallMethodCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
try{
Method setmLanguageMethod = programMonkey.getClass().getMethod("setmLanguage", String.class);
}catch(NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
private long getReflectCallFieldCostTime(int count){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ProgramMonkey programMonkey = new ProgramMonkey("小明", "男", 12);
for(int index = 0 ; index < count; index++){
try{
Field ageField = programMonkey.getClass().getDeclaredField("mLanguage");
}catch(NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
}
沿用上面的测试方法,测试结果如下:
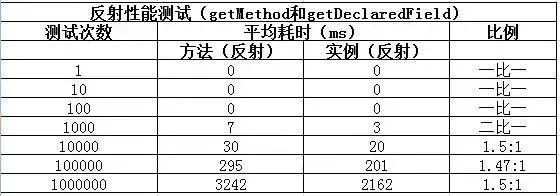
测试结论:
getMethod和getDeclaredField方法会比invoke和set方法耗时;- 随着测试数量级越大,性能差异的比例越趋于稳定;
由于测试的这四个方法最终调用的都是native方法,无法进一步跟踪。个人猜测应该是和在程序运行时操作class有关。
比如需要判断是否安全?是否允许这样操作?入参是否正确?是否能够在虚拟机中找到需要反射的类?主要是这一系列判断条件导致了反射耗时;也有可能是因为调用natvie方法,需要使用JNI接口,导致了性能问题(参照Log.java、System.out.println,都是调用native方法,重复调用多次耗时很明显)。
03 如果避免反射导致的性能问题?
通过上面的测试可以看出,过多地使用反射,的确会存在性能问题,但如果使用得当,所谓反射导致性能问题也就不是问题了,关于反射对性能的影响,参照下面的使用原则,并不会有什么明显的问题:
- 不要过于频繁地使用反射,大量地使用反射会带来性能问题;
- 通过反射直接访问实例会比访问方法快很多,所以应该优先采用访问实例的方式。
04 总结
上面的测试并不全面,但在一定程度上能够反映出反射的确会导致性能问题,也能够大概知道是哪个地方导致的问题。如果后面有必要进一步测试,我会从下面几个方面作进一步测试:
- 测试频繁调用
native方法是否会有明显的性能问题; - 测试同一个方法内,过多的条件判断是否会有明显的性能问题;
- 测试类的复杂程度是否会对反射的性能有明显影响。